At Jobinvietnam.net, we understand that navigating the complexities of Vietnam’s tax system can be daunting, especially for foreigners seeking employment opportunities in this vibrant country. To help you make sense of it all, we’ve put together a comprehensive guide on Vietnam’s income tax rates for both individuals and businesses.

Individual Income Tax Rates in Vietnam
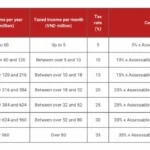
If you’re an individual earning income in Vietnam, you’ll be subject to a progressive tax system. This means that as your income increases, so does your tax rate. Here’s a breakdown of the current individual income tax rates in Vietnam:
| Annual Taxable Income (VND) | Tax Rate |
| Up to 60 million | 5% |
| 60 million to 120 million | 10% |
| 120 million to 216 million | 15% |
| 216 million to 384 million | 20% |
| 384 million to 624 million | 25% |
| 624 million to 960 million | 30% |
| Over 960 million | 35% |
It’s important to note that these tax rates apply to both Vietnamese citizens and foreign residents who earn income in Vietnam. However, foreign residents may be eligible for certain tax exemptions or reductions based on double taxation agreements between Vietnam and their home country.
Corporate Income Tax Rates in Vietnam
For businesses operating in Vietnam, the corporate income tax (CIT) rate is a flat 20%. This rate applies to both domestic and foreign-invested companies. However, there are some exceptions and incentives worth noting:

- Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with annual revenue below VND 20 billion may be eligible for a reduced CIT rate of 17%.
- Companies operating in certain prioritized sectors, such as high-tech, scientific research, or environmental protection, may qualify for CIT incentives, including reduced rates or tax holidays.
- Businesses located in designated economic zones or disadvantaged areas may also benefit from preferential CIT rates and other incentives.
Value-Added Tax (VAT) in Vietnam
In addition to income tax, Vietnam also imposes a value-added tax (VAT) on the supply of goods and services. The standard VAT rate is 10%, but some goods and services are subject to a reduced rate of 5% or are exempt from VAT altogether.
Tax Deductions and Allowances for Individuals in Vietnam
When it comes to tax deductions and allowances, Vietnam offers several options for individuals looking to reduce their taxable income. These include:

- Personal allowance: Individuals are entitled to a personal allowance of VND 11 million per month, which is deducted from their taxable income.
- Dependent allowance: Taxpayers can claim a dependent allowance of VND 4.4 million per month for each eligible dependent, such as children under 18 or elderly parents.
- Charitable contributions: Donations to approved charitable organizations are tax-deductible, subject to certain limits.
- Insurance premiums: Contributions to approved insurance schemes, such as social insurance, health insurance, and unemployment insurance, are deductible from taxable income.
By taking advantage of these deductions and allowances, individuals can effectively lower their tax burden and keep more of their hard-earned income. For a more in-depth look at how these deductions and allowances work, be sure to read our article on Tax Deductions and Allowances for Individuals in Vietnam.
At Jobinvietnam.net, we’re committed to providing you with the most up-to-date and accurate information on Vietnam’s tax system. If you have any questions or need further assistance, don’t hesitate to reach out to our team of experts via phone, Zalo, or WhatsApp. We’re here to help you navigate the world of taxes in Vietnam and ensure that you’re making the most of your employment opportunities in this exciting country.


Determining Tax Residency in Vietnam: A Comprehensive Guide