Tax Compliance and Planning for Individuals and Businesses in Vietnam
At Jobinvietnam.net, we understand the importance of navigating the complex world of tax compliance and planning in Vietnam. Whether you’re an individual or a business, staying on top of your tax obligations is crucial to avoid penalties and ensure smooth operations. In this article, we’ll guide you through the essential aspects of tax compliance and planning in Vietnam.
Understanding the Vietnamese Tax System

businesses and individuals
Vietnam’s tax system is administered by the General Department of Taxation (GDT) under the Ministry of Finance. The country has a progressive tax system, with tax rates varying based on income levels and business types. As an individual or business in Vietnam, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the relevant tax laws and regulations.
Tax Obligations for Individuals
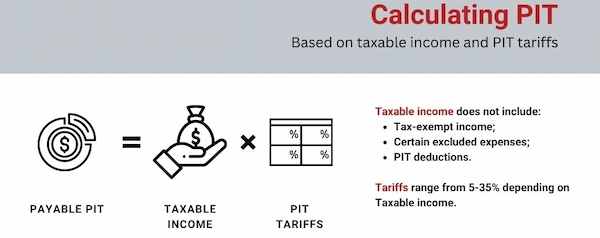
Individuals in Vietnam are subject to personal income tax (PIT) on their worldwide income. The tax rates range from 5% to 35%, depending on the income level. It’s crucial to accurately report your income and file your tax returns on time to avoid penalties.
Tax Obligations for Businesses
Businesses in Vietnam are subject to various taxes, including corporate income tax (CIT), value-added tax (VAT), and foreign contractor tax (FCT). The CIT rate is generally 20%, while the VAT rate ranges from 0% to 10%. It’s essential to maintain accurate financial records and file tax returns within the prescribed deadlines.
Tax Planning Strategies

Effective tax planning can help individuals and businesses minimize their tax liabilities while remaining compliant with the law. Some strategies include:
- Structuring your business in a tax-efficient manner
- Utilizing available tax incentives and exemptions
- Proper record-keeping and documentation
- Seeking professional advice from tax experts
Tax Compliance Procedures
To ensure tax compliance, individuals and businesses must follow the prescribed procedures, such as:
- Registering for tax identification numbers
- Filing tax returns and making payments within the deadlines
- Responding to tax audits and inquiries from the authorities
- Keeping up-to-date with changes in tax laws and regulations
Consequences of Non-Compliance

Failing to comply with Vietnam’s tax laws can result in severe consequences, such as:
- Financial penalties and interest charges
- Legal action and criminal prosecution
- Damage to your reputation and business relationships
- Difficulty in obtaining licenses and permits
Seeking Professional Assistance
Navigating Vietnam’s tax system can be challenging, especially for those unfamiliar with the local laws and regulations. Seeking professional assistance from tax experts can help you:
- Understand your tax obligations and minimize liabilities
- Develop effective tax planning strategies
- Ensure compliance with all relevant laws and regulations
- Represent you in dealings with the tax authorities
At Jobinvietnam.net, we’re committed to providing valuable insights and resources to help individuals and businesses thrive in Vietnam. If you have any questions or need assistance with tax compliance and planning, don’t hesitate to reach out to us via phone, Zalo, or WhatsApp. Our knowledgeable team is ready to provide you with the clearest and most detailed advice tailored to your specific needs.
Determining Tax Residency in Vietnam
Tax residency is a crucial factor in determining an individual’s tax obligations in Vietnam. Generally, an individual is considered a tax resident if they meet one of the following criteria:
- Physically present in Vietnam for 183 days or more within a 12-month period
- Have a permanent residence in Vietnam
- Have a leased residence in Vietnam with a term of 183 days or more within a tax year
Tax residents are subject to personal income tax on their worldwide income, while non-residents are only taxed on their Vietnam-sourced income. Determining your tax residency status is essential to understand your tax obligations and avoid potential penalties. To learn more about the intricacies of determining tax residency in Vietnam, click here to learn more about: Determining Tax Residency in Vietnam



Income Tax Impact on Vietnam Economy | JobinVietnam.net